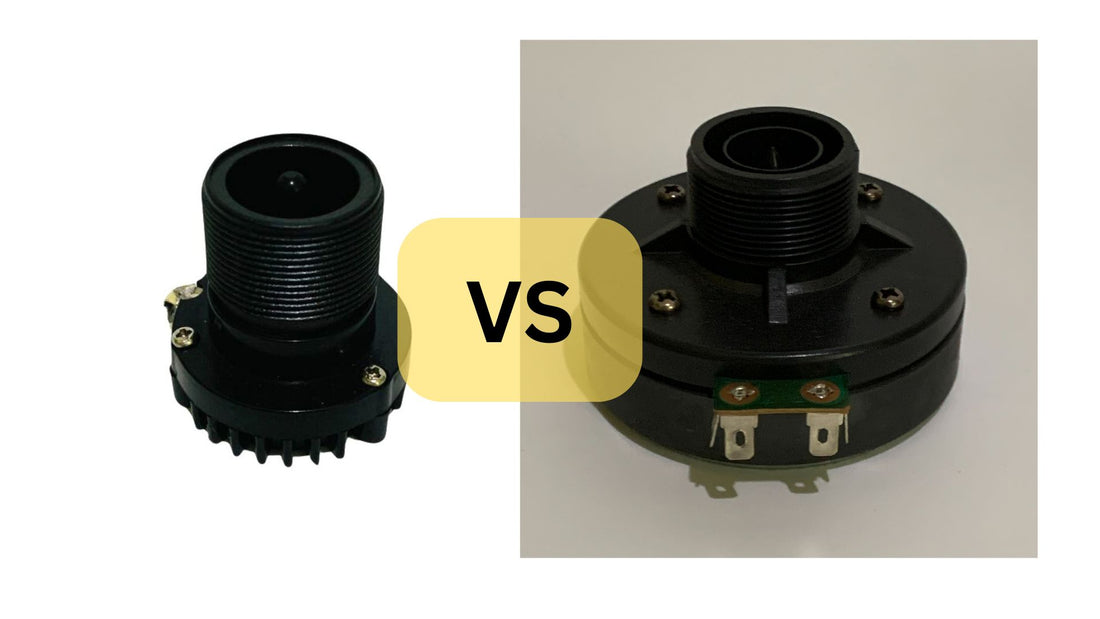
Neodymium vs. Ferrite Magnets in Tweeter Drivers
Share
When designing or selecting a high-quality speaker, especially in the case of a tweeter driver, one crucial factor to consider is the type of magnet used. Two common types of magnets used in speakers are Neodymium (often referred to as "white magnets") and Ferrite magnets (often called "black magnets"). Understanding the differences between these magnets can significantly influence the performance, durability, and cost of a speaker system. In this blog, we will break down these differences, exploring how each magnet affects speaker performance, particularly focusing on the tweeter driver—a key component of any speaker system. We will also delve into the broader components of a speaker to provide a clearer context of how magnets contribute to high-quality sound production.
What is a Tweeter Driver?
Before diving into the details of Neodymium and Ferrite magnets, it’s essential to understand the role of the tweeter driver in a loudspeaker. The tweeter driver, responsible for reproducing high-frequency sounds, is a small but critical component. High frequencies, or treble, range from about 2,000 Hz to 20,000 Hz, and tweeters handle these frequencies to produce clear, sharp sounds such as vocals, cymbals, and the upper harmonics of musical instruments.
The efficiency of the tweeter depends not only on the materials used in the diaphragm or cone but also on the type of magnet that drives the diaphragm. The magnet generates a magnetic field that interacts with the voice coil to produce sound. Hence, the choice between a Neodymium or Ferrite magnet in the tweeter driver significantly influences the sound quality, size, weight, and cost of the speaker.
Neodymium (White Magnet) vs. Ferrite (Black Magnet) Magnets: An Overview
|
Feature |
Neodymium Magnet (White Magnet) |
Ferrite Magnet (Black Magnet) |
|
Magnetic Strength |
High magnetic strength, compact size |
Moderate magnetic strength, larger size |
|
Sound Quality |
Superior high-frequency performance, more detailed sound |
Good performance, but less detailed than Neodymium |
|
Size and Weight |
Smaller and lighter, ideal for portable and compact systems |
Larger and heavier, better suited for stationary systems |
|
Heat Resistance |
Moderate heat resistance, can degrade in extreme heat |
Excellent heat resistance, ideal for high-power systems |
|
Durability |
Durable, but can wear faster in high-heat environments |
Highly durable, especially under continuous use |
|
Cost |
More expensive due to rare earth materials |
Affordable and widely available |
|
Ideal Application |
High-end, compact, or portable speakers |
Larger, budget-friendly, or professional PA systems |
Neodymium Magnets
Neodymium magnets, or white magnets, are part of the rare earth magnet family. Made primarily from Neodymium (Nd), Iron (Fe), and Boron (B), these magnets are known for their incredible strength, lightweight nature, and ability to generate high magnetic fields.

Here’s a closer look at the key characteristics of Neodymium magnets:
- Strength and Efficiency: Neodymium magnets are renowned for their power. A small Neodymium magnet can produce a stronger magnetic field than a much larger Ferrite magnet. This makes it highly efficient for applications like tweeter drivers, where space and precision are crucial. Tweeter drivers built with Neodymium magnets tend to be more responsive, offering enhanced sound detail and clarity at higher frequencies.
- Compact Size: One of the main reasons why Neodymium magnets are favored in high-quality speaker systems is their compact size. Due to their powerful magnetic properties, less material is needed to generate the same level of performance as a larger Ferrite magnet. This allows speaker designers to create smaller and lighter tweeters without compromising on sound quality, making them ideal for compact, high-performance speaker systems.
- Heat Resistance: Neodymium magnets typically have a lower heat tolerance compared to Ferrite magnets, which can lead to degradation in performance over time if exposed to excessive heat. However, modern manufacturing techniques have improved their thermal resistance, making them suitable for most consumer-grade and professional audio applications.
- Cost: Being made from rare earth materials, Neodymium magnets are more expensive to produce than Ferrite magnets. This cost is often reflected in the price of high-quality speaker systems, especially those aimed at audiophiles and professionals who seek the best possible performance.
Ferrite Magnets
Ferrite magnets, or black magnets, are ceramic compounds composed of iron oxide mixed with other elements like barium or strontium. They are much more affordable and have been widely used in speaker systems for decades. Let’s explore their key characteristics:
- Strength and Efficiency: While Ferrite magnets are not as powerful as Neodymium magnets, they still provide enough magnetic force to drive a wide range of speaker components, including woofers and tweeters. In tweeter drivers, Ferrite magnets are slightly less efficient in creating the same sharp high frequencies compared to Neodymium magnets, but they still offer good performance at a fraction of the cost.
- Size and Weight: Due to their lower magnetic strength, Ferrite magnets need to be significantly larger to generate the same output as a Neodymium magnet. As a result, speaker drivers with Ferrite magnets tend to be bulkier and heavier. While this may not be an issue for large home speakers or professional setups, it can be a disadvantage in portable or compact speaker systems where size and weight are crucial factors.
- Heat Resistance: Ferrite magnets have excellent heat resistance, making them ideal for high-power applications where the speaker will be exposed to continuous or intense use. In tweeter drivers, Ferrite magnets maintain consistent performance over extended periods, even in challenging environments like live performances or studio sessions.
- Cost: One of the biggest advantages of Ferrite magnets is their cost. They are much cheaper to produce than Neodymium magnets, making them a popular choice for budget-friendly speaker systems. While they may not offer the same level of performance as Neodymium magnets, they strike a good balance between quality and affordability for most everyday audio applications.
Performance Comparison: Neodymium vs. Ferrite in Tweeter Drivers
Sound Quality
When it comes to high-frequency performance, Neodymium magnets offer superior sound quality. Their ability to produce a stronger magnetic field in a compact space allows for greater control over the movement of the voice coil, resulting in clearer and more detailed sound reproduction. Tweeter drivers with Neodymium magnets tend to have faster transient response, meaning they can more accurately reproduce sharp sounds like cymbals or high-pitched vocals.
On the other hand, Ferrite magnets, while still capable of delivering high frequencies, may lack the precision and clarity of Neodymium-equipped tweeters. This doesn’t mean that Ferrite magnets produce bad sound—they are perfectly adequate for most listeners and applications. However, for audiophiles or professional sound engineers who demand the highest level of detail, Neodymium is the better option.

Durability and Heat Management
As mentioned earlier, Ferrite magnets excel in heat resistance, making them more durable in high-power applications. This makes Ferrite magnets a good choice for tweeters in large speaker systems that handle a lot of power or are used in hot environments, such as outdoor speakers or PA systems.
Neodymium magnets, although improved in heat resistance, can still degrade faster in extreme conditions. However, in typical indoor or moderate-power applications, Neodymium magnets perform exceptionally well without significant heat-related issues.
Size and Portability
If size and portability are important, Neodymium magnets are the clear winner. Their small size and light weight make them perfect for compact tweeter drivers used in portable speaker systems or space-constrained setups. This advantage is especially significant in modern speaker design, where consumers demand smaller, more portable devices without sacrificing sound quality.
Ferrite magnets, being bulkier and heavier, are better suited for stationary speaker systems where size is less of a concern. While they can still be used in tweeters for high-quality audio, their weight and size may not be ideal for portable speaker applications.
Price Considerations
The price difference between Neodymium and Ferrite magnets can be substantial. Neodymium magnets are more expensive due to the rarity of the materials and the complexities involved in their manufacturing. This higher cost is reflected in the price of speaker systems that use Neodymium-based tweeters.
Ferrite magnets, on the other hand, are more affordable, making them a great option for consumers who want good sound quality at a lower price point. Many high-quality speaker systems use Ferrite magnets to keep costs down without sacrificing too much in terms of performance, especially in mid-range or budget audio systems.
Which Magnet is Right for Your Tweeter Driver?
The choice between Neodymium and Ferrite magnets ultimately depends on your priorities and application. For professional audio environments or for audiophiles who demand the best sound quality, Neodymium magnets offer superior performance, particularly in the high-frequency range. Their compact size, light weight, and exceptional sound detail make them ideal for tweeter drivers in high-end speaker systems.
On the other hand, Ferrite magnets provide a more affordable solution without sacrificing too much in terms of durability and sound quality. They are particularly suited for larger, more stationary speaker systems where size and weight are less important, but heat management and cost are critical factors.

Practical Applications of Neodymium and Ferrite Magnets in Speaker Design
- Home Audio Systems: For high-end home audio setups, Neodymium magnets are often preferred due to their compact size and superior sound quality. These systems are typically designed to offer the best possible sound experience, and the extra cost of Neodymium magnets is justified by the performance gains.
- Portable Speakers: Neodymium magnets are a popular choice in portable speakers, where weight and size are major considerations. Tweeter drivers with Neodymium magnets offer excellent high-frequency performance in a lightweight, compact package, making them ideal for Bluetooth speakers, soundbars, and other portable audio devices.
- Professional PA Systems: Ferrite magnets are frequently used in professional PA systems, where speakers are subjected to high power levels and need to withstand heat over long periods. The durability and heat resistance of Ferrite magnets make them a practical choice for large, powerful speaker systems used in live performances or outdoor events.
- Budget Speaker Systems: For consumers looking for affordable speaker solutions, Ferrite magnets provide a good balance of performance and cost. While they may not match the sound quality of Neodymium-based systems, Ferrite magnets still offer solid performance for everyday audio applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Neodymium and Ferrite magnets have their unique strengths and weaknesses when it comes to speaker design, especially in tweeter drivers. Neodymium magnets are known for their compact size, lightweight nature, and superior sound quality, particularly in high-frequency applications like tweeters. These properties make them ideal for audiophiles, professionals, and anyone looking for top-tier audio performance in a smaller, more portable form factor. However, these advantages come at a higher cost, which can be a deterrent for budget-conscious consumers.
Ferrite magnets, on the other hand, provide a more affordable option without compromising too much on performance, especially in larger, stationary systems where size and weight are less of a concern. Their excellent heat resistance and durability make them a solid choice for high-power applications, such as professional PA systems or speakers designed for extended use.
The decision between Neodymium and Ferrite magnets ultimately depends on the specific needs of the speaker system and the priorities of the user. Whether you're designing a custom speaker system from scratch, upgrading an existing setup, or selecting components for a high-end audio experience, understanding the differences between these two types of magnets is crucial for making an informed decision.
Key Takeaways:
- Neodymium magnets offer stronger magnetic fields, compact size, and high-performance sound quality but come at a higher cost.
- Ferrite magnets are larger and heavier but provide a cost-effective and durable solution, particularly suited for larger, high-power systems.
- The tweeter driver, responsible for high-frequency sound production, benefits from the right magnet choice depending on your performance needs and budget.
Whether you're an audiophile, a DIY enthusiast, or a professional in the audio industry, understanding the role of magnets in speaker components can significantly influence the performance of your loudspeakers. Neodymium magnets may be the preferred choice for high-end, high-performance audio systems, while Ferrite magnets remain a reliable and cost-effective option for most other applications.
Choosing the Right Magnet for Your Custom Speaker
If you are looking to build your own custom speaker system, the choice between Neodymium and Ferrite magnets becomes even more critical. Each type of magnet will have a direct impact on the overall sound quality, portability, and longevity of the speaker system you create.
For compact, portable speaker systems where space is at a premium, Neodymium magnets are often the best choice. Their small size and lightweight nature allow for easy integration into smaller enclosures while delivering high-quality sound. They are especially useful in creating high-performance tweeter drivers, where precise sound reproduction is essential.
For larger, stationary speaker systems, Ferrite magnets may be more practical due to their durability, heat resistance, and lower cost. They work particularly well in high-power systems where the speakers need to operate for long periods without losing performance. In these cases, the extra weight and size of Ferrite magnets are less of a concern, especially when the speakers are designed for professional use or are not frequently moved.
Expert Advice on Custom Speaker Components
At DioDIY, we understand that the right speaker components can make all the difference in your audio experience. Whether you are selecting a Neodymium tweeter driver for a compact, high-performance setup or a Ferrite-based system for durability and affordability, our expert team is here to help. With over 20 years of experience in speaker manufacturing and customization, we can provide guidance on which components best suit your needs.
In conclusion, the magnet you choose plays a vital role in shaping the sound quality, size, and durability of your speaker system. Whether you opt for the powerful Neodymium or the reliable Ferrite, understanding their unique characteristics will help you make the best decision for your tweeter driver and overall speaker design. If you need further assistance in customizing your speaker system, feel free to contact DioDIY for expert consultation and design support.








